Labs
Lab 2: A-mazed
Deadlines
-
See labs page
-
To pass this lab you have to give a short demo of your submission to the TAs on 28 Sep 2023; You will have to register for a demo slot by 27 Sep 2023.
Register for one time slot in one of these polls:
Ali, David, Ghaith, Liam, Luca
Use your group number in Fire as name. Please try to split evenly among the available rooms.
For the demo, please join the respective Zoom meeting: Ali, David, Ghaith, Liam, Luca at least 10 minutes before the beginning of your demo and have everything ready to run. Change you name in Zoom to your group number.
All demos are online over Zoom!
Lab description
In this lab, you will have to develop the parallel version of a sequential search algorithm, using the fork/join model. The goal of the search is finding a goal inside a maze taking advantage of parallelism.
Programming language
This lab assignment must be developed in Java.
See the computing resources page for further instructions; make sure you are using Java 8 or newer versions.
Overview
To get started with the lab, download and unpack the material for the lab. To get a better understanding of the problem, run the the sequential version of the search, which is provided as part of the material:
make sequential_smallYou should see a maze in a graphical window with an animated player:
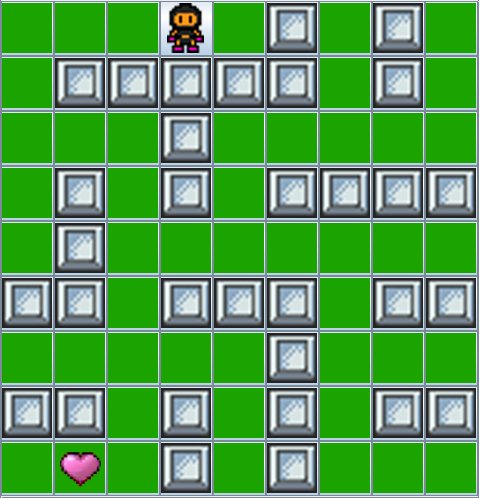
The goal of the search is to find a path that leads from the cell in the top-left corner to a goal, denoted by a heart. All cells colored in green are accessible, whereas cells in grey correspond to walls that cannot be traversed.
In the sequential version of the search, which is the one we started, there is only one player — the little figure that moves around — who will explore all cells until it eventually reaches the goal. Once a goal is found, the program displays the path that leads to it by coloring the cells in red:
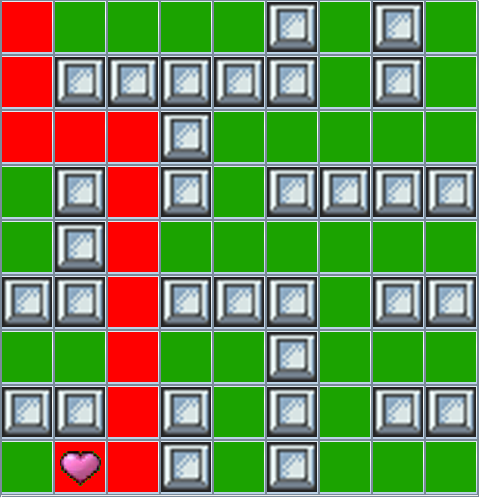
This lab’s objective is to modify the sequential search algorithm using fork/join parallelism to perform the same search but with multiple players concurrently exploring different parts of the maze.
Maze exploration: the API of class Maze
First of all, we should become familiar with the class structure, and in particular with the API of class amazed.maze.Maze. In the material for the lab you can find Javadoc documentation (subdirectory doc) that complements this overview.
Search algorithms interact with an instance of class Maze. Every node (or cell) in the maze has a unique integer identifier. Starting from the initial node, whose identifier is returned by method start(), we can discover the identifiers of new nodes by calling method neighbors(id), which inputs the identifier id of a node we have previously visited, and returns a set of node identifiers, corresponding to all nodes directly adjacent to id and accessible from it. Finally, method hasGoal(id) tests whether id is the identifier of a node containing a goal. If it returns true, we have found a goal!
Node identifiers are randomized at the beginning of every run (even on the same map), which means that they may change from run to run, and that we cannot rely on a fixed mapping between identifiers and positions on a maze’s grid. In fact, if you run the sequential solution multiple times you will probably notice a different sequence of nodes that are visited (it is effectively nondeterministic). Thus, the only option available to build a robust solution is to explore nodes neighborhood by neighborhood, keeping track of the nodes we have already visited.
Strictly speaking, these are the only methods of Maze’s API that are needed to implement a search algorithm. However, it’s nice to keep track of the progress of a search on the graphical animation that we have seen in the sequential version. To do this, we have to add some bookkeping. To explicitly create a new player on a given node id, we call newPlayer(id), which returns a unique identifier of the player. To move a player, we call method move(playerId, id), which moves the player with identifer playerId to node id, provided the latter is accessible and is a neighbor of the node the player is currently in.
Sequential search
Next, let’s have a look at the implementation of class amazed.solver.SequentialSolver, which is the sequential solver algorithm that we have to parallelize. SequentialSolver formally inherits from Java’s RecursiveTask<List<Integer>>, which represents tasks that can be executed in parallel and return a list of integers (see more details in the lecture slides on Parallelizing computations). In the sequential solver, this is just for convenience: SequentialSolver does not actually use any parallelism, but your solution in class ForkJoinSolver can just inherit from SequentialSolver and modify what has to be modified for paralellism, without having to change anything in the class structure.
Class SequentialSolver implements a standard depth-first search. To this end, it uses three data structures to keep track of the state:
-
A set
visitedof identifiers of all nodes visited so far during a search. -
A stack of
frontiernodes, which are all neighbors that have not been visited yet. Using a stack ensures that the most recently discovered neighbors are visited first (LIFO), thus implementing a depth-first search. -
A map
predecessorthat associates to every explored nodenits neighborm, so thatnhas been reached frommduring the search; when this is the case,mmaps toninpredecessor. The mapping is only needed at the end of a search, in order to reconstruct the path from the initial node by following the chain of predecessors.
The method depthFirstSearch() implements the actual search:
-
Start by pushing the start node onto the
frontierstack. -
Repeat until the frontier becomes empty — meaning that all nodes have been explored:
-
Pop a node
currentfromfrontier; this is the node to explore in this iteration. -
Check whether
currentis a goal; if it is, terminate the search successfully. -
Otherwise, add
currenttovisited(if it’s not already visited), move the player there, push all its neighbors onto thefrontierstack, and updatepredecessorwith information about how to reachcurrent’s neighbors.
-
Pop a node
-
Once a goal has been found, method
pathFromTo(from, to)reconstructs a path, as a list of node ids, from nodefromto nodeto(wherefromis the start node andtois a goal node) based on the information previously stored inpredecessor. If no goal is found and all nodes have been explored, returnnull.
How to parallelize the search
This lab’s objective is to implement method parallelSearch() of class ForkJoinSolver so that it implements a parallel version of the sequential search using Java’s fork/join parallelism.
The basic idea is that, at some point during the search, you will fork new threads, and each thread will continue the search in a different part of the maze in parallel to the others. Obviously, a good place to do that is whenever we discover new neighbors: different threads explore different neighbors of the current node. Since ForkJoinSolver is a descendant of Java’s RecursiveTask, to fork a new thread you just create a new instance of ForkJoinSolver, with suitable parameters, and call fork() on the instance.
To design the parallel version of search, start by understanding what state has to be shared among parallel threads. Specifically, you have three data structures that may be shared: a set visited, a stack frontier, and a map predecessor. The threads will have to share some information to synchronize indirectly during the search, but sharing as little as possible helps reduce the possibilities of synchronization errors.
Once you have decided which data structures should be shared, use a thread-safe version of those data structures provided by Java’s standard libraries in java.util.concurrent. For example, for thread-safe sets, use ConcurrentSkipListSet, which implements interface Set. You do not have to implement your own thread-safe version of any data structures for this lab.
Finally, revise the sequential search algorithm so that it forks new threads during the search, and combines the results of their explorations. Since you introduce parallel execution, the order in which nodes in the maze are visited by instances of ForkJoinSolver may not be depth-first as it was in the sequential version; but it is a good idea to start from the sequential depth-first search algorithm as a basis, and add parallelization on top of the natural structure of the problem.
Fine-tuning the degree of parallelism
The constructor of ForkJoinSolver takes a second argument forkAfter, which is an integer that allows us to control the degree of parallelism in our solution.
You are free to ignore this value. However, you may want to use it in your solution to decide when, during a thread’s search, it is time to fork new threads. In fact, a simple approach would be to do it with every new explored cell, but this may be inefficient: forking comes with an overhead, which may grow until it cancels out the speedup advantage of having more threads. We can control the amount of forking using a positive integer forkAfter: search continue sequentially for forkAfter consecutive steps, after which it forks new threads, which will each proceed for forkAfter steps before recursively forking.
The scripts provided with the material for the lab let you test your solution with different values for forkAfter to get an idea of what works better (see Testing your solution).
Assignment
Your assignment is to provide a parallelization of the sequential depth-first search using fork/join parallelism. For this, you need to implement the method parallelSearch() in the class ForkJoinSolver. You should not modify other classes in the given implementation.
-
Submission: Your submission should consist of the following files:
-
ForkJoinSolver.java: the code of the class modified with your solution; make sure your code includes comments -
documentation.txt: a short plain text file describing the rationale of your solution (up to 300 words of text)
-
Please do not submit compressed archives. Just upload the individual files.
Requirements
-
A solution must work correctly, that is it has to always return a path to the goal if a goal is reachable from the initial node, and it has to return
nullotherwise. -
In a correct solution, nodes are to be visited at most once.
-
A correct solution has to terminate in finite time in any maze, and it has to work correctly regardless of the number of physical processors that are available.
-
A correct solution has to work with arbitrary mazes, including mazes with no goals, or with more than one goal (in the latter case, finding any goal is sufficient).
-
A correct solution has to explore a maze by following adjacent nodes. It cannot “guess” a node identifier and, if it corresponds to a valid node jump to it; it also cannot enumerate identifiers until it finds valid ones.
-
A correct solution has to add parallelism to the sequential depth-first search, implemented in method
parallelSearch(), using Java’s fork/join parallelism framework. Task synchronization should mainly occur though invocations of thefork()andjoin()methods on suitable instances of classForkJoinSolver. -
A correct solution has to employ some level of parallelism: at some point during the search, more than one thread has to be active searching on the maze.
-
A correct solution may ignore the parameter
forkAfter. In any case, it has to behave correctly independent of the valueforkAfteris set to inForkJoinSolver’s constructor. -
A correct solution must not contain race conditions or data races.
-
A correct solution must be lock-free: use thread-safe data structures for communication between threads (no semaphores, locks, or synchronized blocks).
Tips and tricks
-
Reuse as much as possible of the existing implementation. In particular, you can reuse the implementation of
pathFromTo, to reconstruct paths between specific nodes that have been visited. -
In order for the search to terminate, and to take advantage of parallelism, it is important that different threads do not revisit nodes that other threads have already visited.
-
After a thread forks new threads, it is also responsible for joining them, that is wait for their termination and combine the results of their work. In particular, a child thread may find a path from an intermediate node to a goal node; it is then the responsibility of the child thread’s parent to combine this partial path with additional information to extend the path all the way back to the start node.
-
It is strongly suggested that you keep track of the new forked tasks as “players” in the graphical animation of the maze. This will help you understand what is going on in the maze. To do this, you have to call
newPlayer(id)for every new thread forked at nodeid; andmove(playerId, id)whenever playerplayerIdmoves from its current node to nodeid. Do not wait until you have a complete solution to add animation: the animation will help you debug partial solutions. -
As we have seen in class, getting an actual measurable speedup with fork/join parallelism may be difficult, and hard to achieve on input that is not really big. The purpose of this lab is to experiment with the logic of fork/join parallelism, not to achieve a significant, measurable speedup on simple examples of mazes.
Testing your solution
Included in the material for the lab are two mazes, “small” and “medium”, on which you can test your solution. Compile your solution and run it with the tests using make:
- Compile your solution:
make compile-
Run your solution on map small, with
forkAfterequal to3or to9:
make parallel_small_step3
make parallel_small_step9-
Run your solution on map medium, with
forkAfterequal to3or to9:
make parallel_medium_step3
make parallel_medium_step9
Compiling and running without make
You can install make following the instructions on the computing resources page. If you do not have make, you can run the examples from the command line after compiling all the project’s source files:
java -cp src/main amazed.Main maps/MAP.map parallel-N
where MAP is small or medium for each of the maps, and N is a positive integer corresponding to the chosen value of forkAfter.
Distinction assignment
NOTE: this assignment is intentionally open-ended
For the distinction assignment, we want you to report on a detailed performance analysis of different approaches to solving this assignment. We expect you to report on what potential bottlenecks might be for the different approaches, and a measure of the time difference between them. To help see the differences better, you might consider creating graphs etc. to visualise the differences between the approaches.
We expect that you to, at the very least, report on the following:
-
Different values of
forkAfter -
Not using
forkAfter, but use something else to decide when to fork - Having the spawning process wait for its children
- Having the spawning process continue to do work
- Custom maps which are much bigger compared to the two samples you have been given
- Varying the amount of workers in the fork/join pool, to see how your solutions scale with respect to the number of processor cores utilized. (This will require a minor modification to the skeleton code.)
- Remember to also evaluate your parallel solutions against the template sequential solution!
It could also be interesting to relax the requirement what nodes are visited at most once – or other variations that trade requirements for performance.
To get good performance analysis, you need to execute your solution without the GUI, as the GUI is a major bottleneck for every solution. To execute your solution without the GUI, use the following command:
java -cp src/main amazed.Main mapFile parallel-N -1
where mapFile is the path to the map and N is the value to forkAfter. -1 is there to suppress the GUI.
For the distinction assignment, please submit the following files (individually, no archives):
-
Your different solutions (
ForkJoinSolver.java) for the different approaches - A report in a readable non-proprietary format (e.g. pdf), where you thoroughly explain what you have done, your results, and an analysis of the result.