GF Resource Grammar Library: Synopsis
B. Bringert and A. Ranta
Introduction
This document contains the most important parts of the GF Resource Grammar API.
It has been machine-generated from the source files; each chapter gives a link
to the relevant source files, which give more information. Some of the files have
not yet been prepared so that the machine generated documentation has the right
format.
Since the character encoding is UTF-8 for Russian and Latin-1 for other
languages, you
may have to change the encoding preference of your browser when reading different
parts of the document.
The second-last chapter gives instructions on how to "browse" the library by
loading the grammars into the gf command editor.
New: Browsing by syntax editor
directly on the web.
The last chapter contains a brief example of how application grammars can
import resource modules. At the same time, it illustrates a "design pattern" for
using the resource API to build functor-based applications
Categories
Source 1: http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/abstract/Common.gf
Source 2: http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/abstract/Cat.gf
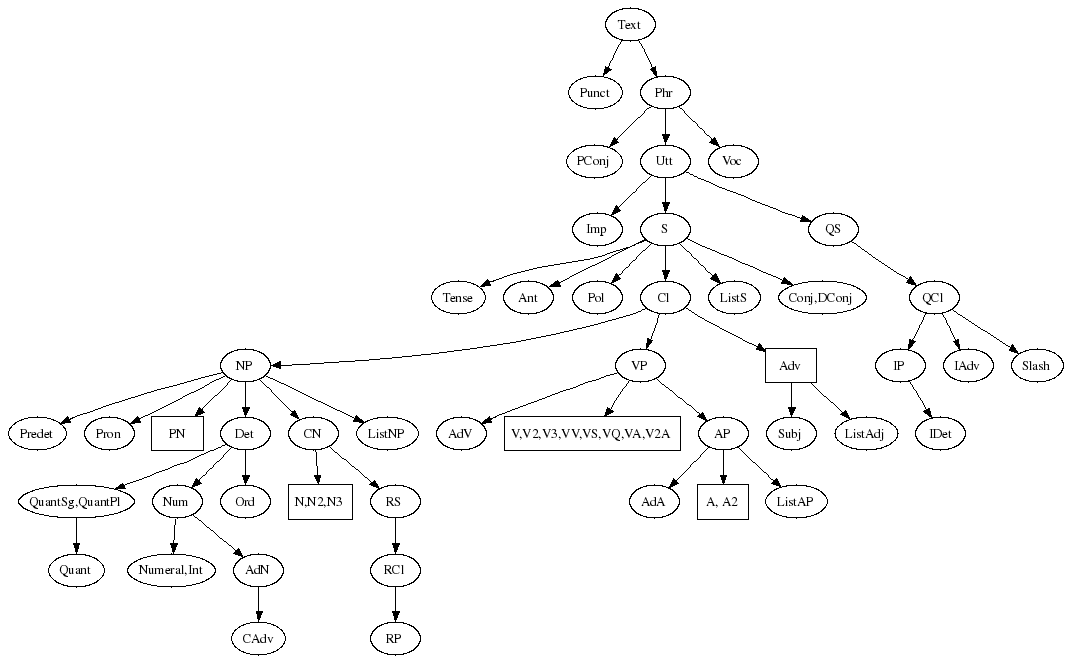
A hierarchic view
The chart below shows the categories in a hierarchical top-down order.
The edges do not define the complete dependency structure; if they did,
the graph would have many many more edges, and also many cycles. The precise
meaning of a directed edge from C to D is: there is a constructor
of C that takes D as an argument. What the constructors exactly are,
and what other arguments they take, is described by separate tables for
each category.
The rectangular boxes mark open lexical categories, which have constructors
also in the Paradigms modules.
Explanations
| Category |
Explanation |
Example |
| A |
one-place adjective |
warm |
| A2 |
two-place adjective |
divisible |
| AP |
adjectival phrase |
very warm |
| AdA |
adjective-modifying adverb |
very |
| AdN |
numeral-modifying adverb |
more than |
| AdV |
adverb directly attached to verb |
always |
| Adv |
verb-phrase-modifying adverb |
in the house |
| Ant |
anteriority |
simultaneous, anterior |
| CAdv |
comparative adverb |
more |
| CN |
common noun (without determiner) |
red house |
| Cl |
declarative clause, with all tenses |
she looks at this |
| Comp |
complement of copula, such as AP |
very warm |
| Conj |
conjunction |
and |
| DConj |
distributed conjunction |
both - and |
| Det |
determiner phrase |
those seven |
| Digits |
cardinal or ordinal in digits |
1,000/1,000th |
| IAdv |
interrogative adverb |
why |
| IComp |
interrogative complement of copula |
where |
| IDet |
interrogative determiner |
which |
| IP |
interrogative pronoun |
who |
| Imp |
imperative |
look at this |
| N |
common noun |
house |
| N2 |
relational noun |
son |
| N3 |
three-place relational noun |
connection |
| NP |
noun phrase (subject or object) |
the red house |
| Num |
cardinal number (used with QuantPl) |
seven |
| Numeral |
cardinal or ordinal in words |
five/fifth |
| Ord |
ordinal number (used in Det) |
seventh |
| PConj |
phrase-beginning conjunction |
therefore |
| PN |
proper name |
Paris |
| Phr |
phrase in a text |
but be quiet please |
| Pol |
polarity |
positive, negative |
| Predet |
predeterminer (prefixed Quant) |
all |
| Prep |
preposition, or just case |
in |
| Pron |
personal pronoun |
she |
| QCl |
question clause, with all tenses |
why does she walk |
| QS |
question |
where did she live |
| Quant |
quantifier ('nucleus' of Det) |
this/these |
| RCl |
relative clause, with all tenses |
in which she lives |
| RP |
relative pronoun |
in which |
| RS |
relative |
in which she lived |
| S |
declarative sentence |
she lived here |
| SC |
embedded sentence or question |
that it rains |
| Slash |
clause missing NP (S/NP in GPSG) |
she looks at |
| Subj |
subjunction |
if |
| Tense |
tense |
present, past, future |
| Text |
text consisting of several phrases |
He is here. Why? |
| Utt |
sentence, question, word... |
be quiet |
| V |
one-place verb |
sleep |
| V2 |
two-place verb |
love |
| V2A |
verb with NP and AP complement |
paint |
| V3 |
three-place verb |
show |
| VA |
adjective-complement verb |
look |
| VP |
verb phrase |
is very warm |
| VQ |
question-complement verb |
ask |
| VS |
sentence-complement verb |
claim |
| VV |
verb-phrase-complement verb |
want |
| Voc |
vocative or "please" |
my darling |
Syntax Rules and Structural Words
Source 1: http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/api/Constructors.gf
Source 2: http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/abstract/Structural.gf
A - one-place adjective
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
A2 - two-place adjective
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
AP - adjectival phrase
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkAP |
A -> AP |
old |
mkAP |
A -> NP -> AP |
older than John |
mkAP |
A2 -> NP -> AP |
married to her |
mkAP |
A2 -> AP |
married to myself |
mkAP |
AP -> S -> AP |
probable that John walks |
mkAP |
AP -> QS -> AP |
uncertain if John walks |
mkAP |
AP -> VP -> AP |
ready to go |
mkAP |
AdA -> A -> AP |
very old |
mkAP |
AdA -> AP -> AP |
very very old |
mkAP |
Conj -> AP -> AP -> AP |
old and big |
mkAP |
Conj -> ListAP -> AP |
old, big, and warm |
mkAP |
DConj -> AP -> AP -> AP |
either old or big |
mkAP |
DConj -> ListAP -> AP |
either old, big, or warm |
AdA - adjective-modifying adverb
| Function |
Type |
Example |
almost_AdA |
AdA |
- |
quite_Adv |
AdA |
- |
so_AdA |
AdA |
- |
too_AdA |
AdA |
- |
very_AdA |
AdA |
- |
AdN - numeral-modifying adverb
| Function |
Type |
Example |
almost_AdN |
AdN |
- |
mkAdN |
CAdv -> AdN |
more than |
AdV - adverb directly attached to verb
| Function |
Type |
Example |
always_AdV |
AdV |
- |
Adv - verb-phrase-modifying adverb
Ant - anteriority
| Function |
Type |
Example |
anteriorAnt |
Ant |
(John has walked) --# notpresent |
simultaneousAnt |
Ant |
(John walks) [default] |
CAdv - comparative adverb
| Function |
Type |
Example |
less_CAdv |
CAdv |
- |
more_CAdv |
CAdv |
- |
CN - common noun (without determiner)
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkCN |
N -> CN |
house |
mkCN |
N2 -> NP -> CN |
mother of John |
mkCN |
N3 -> NP -> NP -> CN |
distance from this city to Paris |
mkCN |
N2 -> CN |
son |
mkCN |
N3 -> CN |
flight |
mkCN |
A -> N -> CN |
big house |
mkCN |
A -> CN -> CN |
big blue house |
mkCN |
AP -> N -> CN |
very big house |
mkCN |
AP -> CN -> CN |
very big blue house |
mkCN |
N -> RS -> CN |
house that John loves |
mkCN |
CN -> RS -> CN |
big house that John loves |
mkCN |
N -> Adv -> CN |
house in the city |
mkCN |
CN -> Adv -> CN |
big house in the city |
mkCN |
CN -> S -> CN |
rule that John walks |
mkCN |
CN -> QS -> CN |
question if John walks |
mkCN |
CN -> VP -> CN |
reason to walk |
mkCN |
N -> NP -> CN |
king John |
mkCN |
CN -> NP -> CN |
old king John |
Cl - declarative clause, with all tenses
| Function |
Type |
Example |
genericCl |
VP -> Cl |
one walks |
mkCl |
NP -> V -> Cl |
John walks |
mkCl |
NP -> V2 -> NP -> Cl |
John loves her |
mkCl |
NP -> V3 -> NP -> NP -> Cl |
John sends it to her |
mkCl |
NP -> VV -> VP -> Cl |
John wants to walk |
mkCl |
NP -> VS -> S -> Cl |
John says that it is good |
mkCl |
NP -> VQ -> QS -> Cl |
John wonders if it is good |
mkCl |
NP -> VA -> AP -> Cl |
John becomes old |
mkCl |
NP -> V2A -> NP -> AP -> Cl |
John paints it red |
mkCl |
NP -> A -> Cl |
John is old |
mkCl |
NP -> A -> NP -> Cl |
John is older than her |
mkCl |
NP -> A2 -> NP -> Cl |
John is married to her |
mkCl |
NP -> AP -> Cl |
John is very old |
mkCl |
NP -> N -> Cl |
John is a man |
mkCl |
NP -> CN -> Cl |
John is an old man |
mkCl |
NP -> NP -> Cl |
John is the man |
mkCl |
NP -> Adv -> Cl |
John is here |
mkCl |
NP -> VP -> Cl |
John walks here |
mkCl |
V -> Cl |
it rains |
mkCl |
VP -> Cl |
it is raining |
mkCl |
N -> Cl |
there is a house |
mkCl |
CN -> Cl |
there is an old houses |
mkCl |
NP -> Cl |
there are five houses |
mkCl |
NP -> RS -> Cl |
it is John that walks |
mkCl |
Adv -> S -> Cl |
it is here John walks |
Comp - complement of copula, such as AP
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
Conj - conjunction
| Function |
Type |
Example |
and_Conj |
Conj |
- |
or_Conj |
Conj |
- |
DConj - distributed conjunction
| Function |
Type |
Example |
both7and_DConj |
DConj |
- |
either7or_DConj |
DConj |
- |
Det - determiner phrase
Digits - cardinal or ordinal in digits
IAdv - interrogative adverb
IComp - interrogative complement of copula
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
IDet - interrogative determiner
| Function |
Type |
Example |
how8many_IDet |
IDet |
- |
whichPl_IDet |
IDet |
- |
whichSg_IDet |
IDet |
- |
IP - interrogative pronoun
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkIP |
IDet -> N -> IP |
which city |
mkIP |
IDet -> (Num) -> (Ord) -> CN -> IP |
which five best cities |
mkIP |
IP -> Adv -> IP |
who in Paris |
whatPl_IP |
IP |
- |
whatSg_IP |
IP |
- |
whoPl_IP |
IP |
- |
whoSg_IP |
IP |
- |
Imp - imperative
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkImp |
V -> Imp |
go |
mkImp |
V2 -> NP -> Imp |
take it |
mkImp |
VP -> Imp |
go there now |
ImpForm
| Function |
Type |
Example |
pluralImpForm |
ImpForm |
(help yourselves) |
politeImpForm |
ImpForm |
(help yourself) (polite singular) |
singularImpForm |
ImpForm |
(help yourself) [default] |
ListAP
ListAdv
ListNP
ListS
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkListS |
S -> S -> ListS |
he walks, I run |
mkListS |
S -> ListS -> ListS |
John walks, I run, you sleep |
N - common noun
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
N2 - relational noun
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
N3 - three-place relational noun
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
NP - noun phrase (subject or object)
Num - cardinal number (used with QuantPl)
Numeral - cardinal or ordinal in words
Ord - ordinal number (used in Det)
PConj - phrase-beginning conjunction
PN - proper name
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
Phr - phrase in a text
Pol - polarity
| Function |
Type |
Example |
negativePol |
Pol |
(John doesn't walk) |
positivePol |
Pol |
(John walks) [default] |
Predet - predeterminer (prefixed Quant)
Prep - preposition, or just case
Pron - personal pronoun
Punct
| Function |
Type |
Example |
exclMarkPunct |
Punct |
! |
fullStopPunct |
Punct |
. |
questMarkPunct |
Punct |
? |
QCl - question clause, with all tenses
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkQCl |
Cl -> QCl |
does John walk |
mkQCl |
IP -> VP -> QCl |
who walks |
mkQCl |
IP -> NP -> V2 -> QCl |
whom does John love |
mkQCl |
IP -> Slash -> QCl |
whom does John love today |
mkQCl |
IAdv -> Cl -> QCl |
why does John walk |
mkQCl |
Prep -> IP -> Cl -> QCl |
with who does John walk |
mkQCl |
IAdv -> NP -> QCl |
where is John |
mkQCl |
IP -> QCl |
what is there |
QS - question
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkQS |
QCl -> QS |
who walks |
mkQS |
(Tense) -> (Ant) -> (Pol) -> QCl -> QS |
who wouldn't have walked |
mkQS |
Cl -> QS |
does John walk |
Quant - quantifier ('nucleus' of Det)
QuantPl
QuantSg
RCl - relative clause, with all tenses
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkRCl |
RP -> VP -> RCl |
that walk |
mkRCl |
RP -> NP -> V2 -> RCl |
which John loves |
mkRCl |
RP -> Slash -> RCl |
which John loves today |
mkRCl |
Cl -> RCl |
such that John loves her |
RP - relative pronoun
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkRP |
Prep -> NP -> RP -> RP |
all the houses in which |
which_RP |
RP |
which |
RS - relative
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkRS |
RCl -> RS |
that walk |
mkRS |
(Tense) -> (Ant) -> (Pol) -> RCl -> RS |
that wouldn't have walked |
S - declarative sentence
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkS |
Cl -> S |
John walks |
mkS |
(Tense) -> (Ant) -> (Pol) -> Cl -> S |
John wouldn't have walked |
mkS |
Conj -> S -> S -> S |
John walks and I run |
mkS |
Conj -> ListS -> S |
John walks, I run and you sleep |
mkS |
DConj -> S -> S -> S |
either John walk or I run |
mkS |
DConj -> ListS -> S |
either John walks, I run or you sleep |
mkS |
Adv -> S -> S |
today, John walks |
SC - embedded sentence or question
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
Slash - clause missing NP (S/NP in GPSG)
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkSlash |
NP -> V2 -> Slash |
(whom) John loves |
mkSlash |
NP -> VV -> V2 -> Slash |
(whom) John wants to see |
mkSlash |
Cl -> Prep -> Slash |
(with whom) John walks |
mkSlash |
Slash -> Adv -> Slash |
(whom) John loves today |
Subj - subjunction
| Function |
Type |
Example |
although_Subj |
Subj |
- |
because_Subj |
Subj |
- |
if_Subj |
Subj |
- |
when_Subj |
Subj |
- |
Tense - tense
| Function |
Type |
Example |
conditionalTense |
Tense |
(John would walk) --# notpresent |
futureTense |
Tense |
(John will walk) --# notpresent |
pastTense |
Tense |
(John walked) --# notpresent |
presentTense |
Tense |
(John walks) [default] |
Text - text consisting of several phrases
Utt - sentence, question, word...
V - one-place verb
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
V2 - two-place verb
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
V2A - verb with NP and AP complement
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
V3 - three-place verb
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
VA - adjective-complement verb
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
VP - verb phrase
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkVP |
V -> VP |
walk |
mkVP |
V2 -> NP -> VP |
love her |
mkVP |
V3 -> NP -> NP -> VP |
send it to her |
mkVP |
VV -> VP -> VP |
want to walk |
mkVP |
VS -> S -> VP |
know that she walks |
mkVP |
VQ -> QS -> VP |
ask if she walks |
mkVP |
VA -> AP -> VP |
become old |
mkVP |
V2A -> NP -> AP -> VP |
paint it red |
mkVP |
A -> VP |
be warm |
mkVP |
AP -> VP |
be very warm |
mkVP |
A -> NP -> VP |
be older than her |
mkVP |
A2 -> NP -> VP |
be married to her |
mkVP |
N -> VP |
be a man |
mkVP |
CN -> VP |
be an old man |
mkVP |
NP -> VP |
be the man |
mkVP |
Adv -> VP |
be here |
mkVP |
VP -> Adv -> VP |
sleep here |
mkVP |
AdV -> VP -> VP |
always sleep |
passiveVP |
V2 -> VP |
be loved |
passiveVP |
V2 -> NP -> VP |
be loved by her |
progressiveVP |
VP -> VP |
be sleeping |
reflexiveVP |
V2 -> VP |
love itself |
VQ - question-complement verb
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
VS - sentence-complement verb
Lexical category, constructors given in
lexical paradigms.
VV - verb-phrase-complement verb
| Function |
Type |
Example |
can8know_VV |
VV |
- |
can_VV |
VV |
- |
must_VV |
VV |
- |
want_VV |
VV |
- |
Voc - vocative or "please"
| Function |
Type |
Example |
mkVoc |
NP -> Voc |
John |
please_Voc |
Voc |
- |
Lexical Paradigms
Paradigms for Danish
source http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/danish/ParadigmsDan.gf
| Function |
Type |
Gender |
Type |
utrum |
Gender |
neutrum |
Gender |
Number |
Type |
singular |
Number |
plural |
Number |
Case |
Type |
nominative |
Case |
genitive |
Case |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
noPrep |
Prep |
mkN |
(bil : Str) -> N |
mkN |
(hus : Str) -> Gender -> N |
mkN |
(bil,bilen : Str) -> N |
mkN |
(bil,bilen,biler : Str) -> N |
mkN |
(dreng,drengen,drenge,drengene : Str) -> N |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
regN2 |
Str -> Gender -> N2 |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
mkA |
(fin : Str) -> A |
mkA |
(fin,fint : Str) -> A |
mkA |
(galen,galet,galne : Str) -> A |
mkA |
(stor,stort,store,storre,storst : Str) -> A |
mkA |
A -> A |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
mkV |
(snakke : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(leve,levde : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(drikke, drakk, drukket : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(spise,spiser,spises,spiste,spist,spis : Str) -> V |
mkV |
V -> Str -> V |
vaereV |
V -> V |
depV |
V -> V |
reflV |
V -> V |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
mkV0 |
V -> V0 |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
mkAS |
A -> AS |
mkA2S |
A -> Prep -> A2S |
mkAV |
A -> AV |
mkA2V |
A -> Prep -> A2V |
Paradigms for English
source http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/english/ParadigmsEng.gf
| Function |
Type |
Gender |
Type |
human |
Gender |
nonhuman |
Gender |
masculine |
Gender |
Number |
Type |
singular |
Number |
plural |
Number |
Case |
Type |
nominative |
Case |
genitive |
Case |
mkN |
(flash : Str) -> N |
mkN |
(man,men : Str) -> N |
mkN |
(man,men,man's,men's : Str) -> N |
mkN |
Str -> N -> N |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
regN2 |
Str -> N2 |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
mkA |
(happy : Str) -> A |
mkA |
(fat,fatter : Str) -> A |
mkA |
(good,better,best,well : Str) -> A |
compoundA |
A -> A |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
noPrep |
Prep |
mkV |
(cry : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(stop, stopped : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(drink, drank, drunk : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(run, ran, run, running : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(go, goes, went, gone, going : Str) -> V |
partV |
V -> Str -> V |
reflV |
V -> V |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
mkV0 |
V -> V0 |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
mkAS |
A -> AS |
mkA2S |
A -> Prep -> A2S |
mkAV |
A -> AV |
mkA2V |
A -> Prep -> A2V |
Paradigms for Finnish
source http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/finnish/ParadigmsFin.gf
| Function |
Type |
Number |
Type |
singular |
Number |
plural |
Number |
Case |
Type |
nominative |
Case |
genitive |
Case |
partitive |
Case |
translative |
Case |
inessive |
Case |
elative |
Case |
illative |
Case |
adessive |
Case |
ablative |
Case |
allative |
Case |
prePrep |
Case -> Str -> Prep |
postPrep |
Case -> Str -> Prep |
postGenPrep |
Str -> Prep |
casePrep |
Case -> Prep |
mkN |
(talo : Str) -> N |
mkN |
(savi,savia : Str) -> N |
mkN |
(vesi,veden,vesiä : Str) -> N |
mkN |
(olo,oln,olona,oloa,oloon,oloina,oloissa,olojen,oloja,oloihin : Str) -> N |
sgpartN |
(meri : N) -> (merta : Str) -> N |
nMeri |
(meri : Str) -> N |
nKukko |
(kukko,kukon,kukkoja : Str) -> N |
nTalo |
(talo : Str) -> N |
nLukko |
(lukko : Str) -> N |
nArpi |
(arpi : Str) -> N |
nSylki |
(sylki : Str) -> N |
nLinux |
(linuxia : Str) -> N |
nPeruna |
(peruna : Str) -> N |
nRae |
(rae, rakeena : Str) -> N |
nSusi |
(susi,suden,sutta : Str) -> N |
nPuu |
(puu : Str) -> N |
nSuo |
(suo : Str) -> N |
nNainen |
(naista : Str) -> N |
nTilaus |
(tilaus,tilauksena : Str) -> N |
nKulaus |
(kulaus : Str) -> N |
nNauris |
(naurista : Str) -> N |
compN |
Str -> N -> N |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 = genN2 |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 = mmkN2 |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
mkA |
Str -> A |
mkA |
N -> A |
mkA |
N -> (kivempaa,kivinta : Str) -> A |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
mkV |
(soutaa : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(soutaa,souti : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(soutaa,soudan,souti : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(tulla,tulee,tulen,tulevat,tulkaa,tullaan,tuli,tulin,tulisi,tullut,tultu,tullun : Str) -> V |
mkV |
V -> Case -> V |
vValua |
(valua : Str) -> V |
vKattaa |
(kattaa, katan : Str) -> V |
vOstaa |
(ostaa : Str) -> V |
vNousta |
(nousta, nousen : Str) -> V |
vTuoda |
(tuoda : Str) -> V |
caseV |
Case -> V -> V |
vOlla |
V |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> Case -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
dirV3 |
V -> Case -> V3 |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
mkV0 |
V -> V0 |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> V2V |
mkVA |
V -> Prep -> VA |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2A |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
mkAS |
A -> AS |
mkA2S |
A -> Prep -> A2S |
mkAV |
A -> AV |
mkA2V |
A -> Prep -> A2V |
Paradigms for French
source http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/french/ParadigmsFre.gf
Paradigms for German
source http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/german/ParadigmsGer.gf
| Function |
Type |
Gender |
Type |
masculine |
Gender |
feminine |
Gender |
neuter |
Gender |
Case |
Type |
nominative |
Case |
accusative |
Case |
dative |
Case |
genitive |
Case |
Number |
Type |
singular |
Number |
plural |
Number |
mkN |
(Stufe : Str) -> N |
mkN |
(Bild,Bilder : Str) -> Gender -> N |
mkN |
(x1,_,_,_,_,x6 : Str) -> Gender -> N |
mkN2 |
Str -> N2 |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
mkPN |
(nom,gen : Str) -> PN |
mkPN |
(nom,acc,dat,gen : Str) -> PN |
mkA |
Str -> A |
mkA |
(gut,besser,beste : Str) -> A |
invarA |
Str -> A |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
mkPrep |
Str -> Case -> Prep |
accPrep |
Prep |
datPrep |
Prep |
genPrep |
Prep |
von_Prep |
Prep |
zu_Prep |
Prep |
mkV |
(führen : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(sehen,sieht,sah,sähe,gesehen : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(geben, gibt, gib, gab, gäbe, gegeben : Str) -> V |
mkV |
Str -> V -> V |
no_geV |
V -> V |
seinV |
V -> V |
habenV |
V -> V |
reflV |
V -> Case -> V |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> Case -> V2 |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
accdatV3 |
V -> V3 |
mkV0 |
V -> V0 |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> V2V |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
mkAS |
A -> AS |
mkA2S |
A -> Prep -> A2S |
mkAV |
A -> AV |
mkA2V |
A -> Prep -> A2V |
Paradigms for Italian
source http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/italian/ParadigmsIta.gf
| Function |
Type |
Gender |
Type |
masculine |
Gender |
feminine |
Gender |
Number |
Type |
singular |
Number |
plural |
Number |
--Prep |
Type |
accusative |
Prep |
genitive |
Prep |
dative |
Prep |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
mkN |
(cane : Str) -> N |
mkN |
(carne : Str) -> Gender -> N |
mkN |
(uomo,uomini : Str) -> Gender -> N |
mkN |
N -> Str -> N |
mkN2 |
Str -> N2 |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
mkA |
(bianco : Str) -> A |
mkA |
(solo,sola,soli,sole,solamente : Str) -> A |
mkA |
A -> A -> A |
prefixA |
A -> A = prefA |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
mkV |
Str -> V |
mkV |
Verbo -> V |
mkV |
(udire,odo,ode,udiamo,udiro,udii,udisti,udi,udirono,odi,udito : Str) -> V |
essereV |
V -> V |
reflV |
V -> V |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
v2V |
V2 -> V |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
mkV0 |
V -> V0 |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
deVV |
V -> VV |
aVV |
V -> VV |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2A |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
mkAS |
A -> AS |
mkA2S |
A -> Prep -> A2S |
mkAV |
A -> Prep -> AV |
mkA2V |
A -> Prep -> Prep -> A2V |
Paradigms for Norwegian
source http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/norwegian/ParadigmsNor.gf
| Function |
Type |
Gender |
Type |
masculine |
Gender |
feminine |
Gender |
neutrum |
Gender |
Number |
Type |
singular |
Number |
plural |
Number |
Case |
Type |
nominative |
Case |
genitive |
Case |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
noPrep |
Prep |
mkN |
Str -> N |
mkN |
Str -> Gender -> N |
mkN |
(bil,bilen : Str) -> N |
mkN |
(dreng,drengen,drenger,drengene : Str) -> N |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
regN2 |
Str -> Gender -> N2 |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
mkPN |
N -> PN |
mkA |
(fin : Str) -> A |
mkA |
(fin,fint : Str) -> A |
mkA |
(galen,galet,galne : Str) -> A |
mkA |
(stor,stort,store,storre,storst : Str) -> A |
mkA |
A -> A |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
mkV |
(snakke : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(leve,levde : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(drikke, drakk, drukket : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(spise,spiser,spises,spiste,spist,spis : Str) -> V |
mkV |
V -> Str -> V |
vaereV |
V -> V |
depV |
V -> V |
reflV |
V -> V |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
dirV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
dirdirV3 |
V -> V3 |
mkV0 |
V -> V0 |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
mkAS |
A -> AS |
mkA2S |
A -> Prep -> A2S |
mkAV |
A -> AV |
mkA2V |
A -> Prep -> A2V |
Paradigms for Russian
source http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/russian/ParadigmsRus.gf
| Function |
Type |
Gender |
Type |
masculine |
Gender |
feminine |
Gender |
neuter |
Gender |
Case |
Type |
nominative |
Case |
genitive |
Case |
dative |
Case |
accusative |
Case |
instructive |
Case |
prepositional |
Case |
Number |
Type |
singular |
Number |
plural |
Number |
mkN |
(nomSg, genSg, datSg, accSg, instSg, preposSg, prepos2Sg, |
regN |
Str -> N |
nMashina |
Str -> N |
nEdinica |
Str -> N |
nZhenchina |
Str -> N |
nNoga |
Str -> N |
nMalyariya |
Str -> N |
nTetya |
Str -> N |
nBol |
Str -> N |
nObezbolivauchee |
Str -> N |
nProizvedenie |
Str -> N |
nChislo |
Str -> Str -> N |
nZhivotnoe |
Str -> N |
nPepel |
Str -> N |
nMalush |
Str -> N |
nPotolok |
Str -> N |
nStomatolog |
Str -> N |
nAdres |
Str -> N |
nTelefon |
Str -> N |
nNol |
Str -> N |
nUchitel |
Str -> N |
nUroven |
Str -> N |
nSlovar |
Str -> N |
nMusej |
Str -> N |
nDvorec |
Str -> N |
nTovarish |
Str -> N |
nMesjac |
Str -> N |
nGrazhdanin |
Str -> N |
nRebenok |
Str -> N |
nPut |
Str -> N |
nGospodin |
Str -> N |
nDen |
Str -> N |
nDrug |
Str -> N |
nSyn |
Str -> N |
nLes |
Str -> N |
nMost |
Str -> N |
mkFun |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
mkN2 |
N -> N2 |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> Animacy -> PN |
nounPN |
N -> PN |
regA |
Str -> Str -> A |
adjInvar |
Str -> A |
AStaruyj |
Str -> Str -> A |
AMalenkij |
Str -> Str -> A |
AKhoroshij |
Str -> Str -> A |
AMolodoj |
Str -> Str -> A |
AKakoj_Nibud |
Str -> Str -> Str -> A |
mkA2 |
A -> Str -> Case -> A2 |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
mkV |
Aspect -> (presentSgP1,presentSgP2,presentSgP3, |
pastSgP1,imperative,infinitive |
Str) -> V |
mkV2 |
V -> Str -> Case -> V2 |
mkV3 |
V -> Str -> Str -> Case -> Case -> V3 |
dirV2 |
V -> V2 |
tvDirDir |
V -> V3 |
Paradigms for Spanish
source http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/spanish/ParadigmsSpa.gf
Paradigms for Swedish
source http://www.cs.chalmers.se/~aarne/GF/lib/resource/swedish/ParadigmsSwe.gf
| Function |
Type |
Gender |
Type |
utrum |
Gender |
neutrum |
Gender |
Number |
Type |
singular |
Number |
plural |
Number |
Case |
Type |
nominative |
Case |
genitive |
Case |
mkPrep |
Str -> Prep |
noPrep |
Prep |
mkN |
(apa : Str) -> N |
mkN |
(lik : Str) -> Gender -> N |
mkN |
(nyckel,nycklar : Str) -> N |
mkN |
(museum,museet,museer,museerna : Str) -> N |
mkN2 |
Str -> N2 |
mkN2 |
N -> Prep -> N2 |
mkN3 |
N -> Prep -> Prep -> N3 |
mkPN |
Str -> PN |
mkPN |
Str -> Gender -> PN |
mkPN |
(jesus,jesu : Str) -> Gender -> PN |
mkA |
(billig : Str) -> A |
mkA |
(bred,brett : Str) -> A |
mkA |
(tung,tyngre,tyngst : Str) -> A |
mkA |
(god,gott,goda,battre,bast : Str) -> A |
mkA |
(liten,litet,lilla,sma,mindre,minst,minsta : Str) -> A |
compoundA |
A -> A |
mkA2 |
A -> Prep -> A2 |
mkAdv |
Str -> Adv |
mkAdV |
Str -> AdV |
mkAdA |
Str -> AdA |
mkV |
(stämmer : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(dricka,drack,druckit : Str) -> V |
mkV |
(gå,går,gå,gick,gått,gången : Str) -> V |
mkV |
V -> Str -> V |
depV |
V -> V |
reflV |
V -> V |
mkV2 |
Str -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> V2 |
mkV2 |
V -> Prep -> V2 |
mkV3 |
Str -> V3 |
mkV3 |
V -> V3 |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> V3 |
mkV3 |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V3 |
mkV0 |
V -> V0 |
mkVS |
V -> VS |
mkV2S |
V -> Prep -> V2S |
mkVV |
V -> VV |
mkV2V |
V -> Prep -> Prep -> V2V |
mkVA |
V -> VA |
mkV2A |
V -> Prep -> V2A |
mkVQ |
V -> VQ |
mkV2Q |
V -> Prep -> V2Q |
mkAS |
A -> AS |
mkA2S |
A -> Prep -> A2S |
mkAV |
A -> AV |
mkA2V |
A -> Prep -> A2V |
Browsing the libraries with GF commands
New: Browsing by syntax editor
directly on the web.
All of the following assume
cd $GF_LIB_PATH
To try out inflection paradigms:
> i -path=alltenses:prelude -retain alltenses/ParadigmsGer.gfr
> cc mkN "Farbe"
To try out overloaded syntax, test lexicon, and inflection paradigms:
> i -path=alltenses:prelude -retain alltenses/TryGer.gfr
> cc mkCl (mkNP this_QuantSg (mkN "Farbe")) (mkA "dunkel")
To look for a syntax tree in the overload API by parsing:
> i -path=alltenses:prelude alltenses/OverLangEng.gfc
> p -cat=S -overload "this grammar is too big"
To view linearizations in all languages by parsing from English:
> i alltenses/langs.gfcm
> p -cat=S -lang=LangEng "this grammar is too big" | tb
An Example of Usage
The standard way of building an application has the following modules.
An abstract syntax:
abstract Music = {
cat
Kind,
Property ;
fun
PropKind : Kind -> Property -> Kind ;
Song : Kind ;
American : Property ;
}
A domain lexicon interface:
interface LexMusic = open Cat in {
oper
song_N : N ;
american_A : A ;
}
A functor on Syntax and the domain lexicon interface:
incomplete concrete MusicI of Music = open Syntax, MusicLex in {
lincat
Kind = CN ;
Property = AP ;
lin
PropKind k p = mkCN p k ;
Song = mkCN song_N ;
American = mkAP american_A ;
}
For each language, an instance of the domain lexicon:
instance LexMusicGer of LexMusic = CatGer ** open ParadigmsGer in {
oper
song_N = mkN "Lied" "Lieder" neuter ;
american_A = mkA "amerikanisch" ;
}
For each language, an instantiation of the functor:
--# -path=.:present:prelude
concrete MusicGer of Music = MusicI with
(Syntax = SyntaxGer),
(LexMusic = LexMusicGer) ;