| Maintainer | Thomas Hallgren |
|---|---|
| Stability | Experimental |
| Safe Haskell | None |
ThreepennyFudgets
Contents
Description
Threepenny Fudgets is a prototype library for writing GUI applications in a functional style in Haskell, using a web browser for the user interface.
Threepenny Fudgets is based on Fudgets (a Graphical User Interface Libary for Haskell developed in the early 1990s) but has a completely separate implementation on top of threepenny-gui.
- data F hi ho
- type (+) a b = Either a b
- fromLeft :: Either a b -> Maybe a
- fromRight :: Either b a -> Maybe a
- type URL = String
- runF :: F hi ho -> IO ()
- runF' :: (Window -> UI a) -> F hi p -> IO ()
- buttonF :: String -> F Click Click
- data Click = Click
- buttonGroupF :: F hi ho -> F (Click + hi) (Click + ho)
- toggleButtonF :: String -> F Bool Bool
- checkboxF :: F Bool Bool
- radioGroupF :: Eq alt => Options alt -> F alt alt
- radioGroupF' :: Eq alt => Options alt -> F alt alt
- selectF :: Eq alt => Options alt -> F alt alt
- data Options alt = Options [(alt, String)] alt
- dynSelectF :: Eq alt => Options alt -> SelectF alt
- type SelectF alt = F (ListRequest alt) alt
- data ListRequest alt
- sliderF :: Enum a => (a, a) -> F a a
- progressF :: (Num i, Ord i, Show i) => i -> F i o
- meterF :: (Num i, Ord i, Show i) => (i, i) -> F i o
- stringDisplayF :: F String ho
- htmlDisplayF :: F String ho
- showF :: Show i => F i o
- numberF :: (Show a, Read a, Num a) => F a a
- readShowF :: (Show a, Read a) => F a a
- stringF :: F String String
- passwordF :: F String String
- canvasF :: (Int, Int) -> F (Picture ()) (Int, Int)
- canvasF' :: (Int, Int) -> F (Bool, Picture ()) (Int, Int)
- imgF :: URL -> F URL o
- imgF' :: Attribute -> URL -> F URL o
- focusF :: F hi ho -> F (Bool + hi) (Bool + ho)
- disableF :: F hi ho -> F (Bool + hi) ho
- eventF :: [Element -> Event b] -> ((Element -> Event b, b) -> ho) -> F hi ho -> F hi ho
- textF :: String -> F hi ho
- htmlF :: String -> F hi ho
- ahrefF :: URL -> F i o -> F i o
- h1F :: F hi ho -> F hi ho
- h2F :: F hi ho -> F hi ho
- h3F :: F hi ho -> F hi ho
- h4F :: F hi ho -> F hi ho
- pF :: F hi ho -> F hi ho
- tableF :: Int -> F hi ho -> F hi ho
- divF :: F hi ho -> F hi ho
- boxF :: F hi ho -> F hi ho
- ulF :: F hi ho -> F hi ho
- olF :: F hi ho -> F hi ho
- liF :: F hi ho -> F hi ho
- preF :: F hi ho -> F hi ho
- permuteF :: ([Element] -> [Element]) -> F hi ho -> F hi ho
- shellF :: String -> F hi ho -> F hi ho
- vBoxF :: F hi ho -> F hi ho
- hBoxF :: F hi ho -> F hi ho
- classF :: F hi ho -> String -> F hi ho
- withF :: F hi ho -> [Attribute] -> F hi ho
- dynWithF :: F hi ho -> F ([Attribute] + hi) ho
- dynF :: F i o -> F (F i o + i) o
- (>+<) :: F i1 o1 -> F i2 o2 -> F (i1 + i2) (o1 + o2)
- (>+) :: F hi1 ho -> F hi2 p -> F hi1 ho
- (+<) :: F hi1 p -> F hi2 ho -> F hi2 ho
- listF :: Eq a => [(a, F hi b)] -> F (a, hi) (a, b)
- (=<=) :: F hi1 ho -> F hi2 hi1 -> F hi2 ho
- (=>=) :: F hi1 hi2 -> F hi2 ho -> F hi1 ho
- loopLeftF :: F (loop + hi) (loop + ho) -> F hi ho
- loopF :: F ho ho -> F ho ho
- loopThroughRightF :: F (Either a hi) (Either b ho) -> F b a -> F hi ho
- mapF :: (a -> ho) -> F a ho
- filterF :: (ho -> Bool) -> F ho ho
- mapMaybeF :: (a -> Maybe ho) -> F a ho
- concatMapF :: (i -> [o]) -> F i o
- stateF :: (s -> hi -> (s, [ho])) -> s -> F hi ho
- persistentStateF :: (Read s, Show s) => String -> (s -> i -> (s, [o])) -> s -> F i o
- localStorageF :: (Read a, Show a) => String -> a -> F a a
- putF :: ho -> F hi ho -> F hi ho
- putsF :: [ho] -> F hi ho -> F hi ho
- nullF :: F p ho
- idF :: F hi hi
- concatF :: F [i] i
- toBothF :: F a (a + a)
- throughF :: F ho ho -> F ho ho
- splitF :: F (a, b) (a + b)
- gatherF :: F (a + b) (a, b)
- gatherF' :: (a, b) -> F (a + b) (a, b)
- timerF :: F (Maybe Int) Tick
- data Tick = Tick
- writeLogF :: (hi -> String) -> F hi hi
- initF :: UI a -> (a -> F hi ho) -> F hi ho
- ioF :: (hi -> IO ho) -> F hi ho
- elemDisplayF :: Maybe (UI Element -> UI a) -> F (UI Element -> UI b) o
- modifyF :: (H ho -> [Element] -> UI [Element]) -> F hi ho -> F hi ho
- type H a = a -> UI ()
- type Attribute = UI Element -> UI Element
- (=:) :: ReadWriteAttr Element i o -> i -> Attribute
- attr :: String -> WriteAttr Element String
- style :: WriteAttr Element [(String, String)]
- setMany :: [Attribute] -> Attribute
- type Picture a = Canvas -> UI a
- type Point = (Double, Double)
- circle :: Point -> Double -> Canvas -> UI ()
- line :: Point -> Point -> Picture ()
- strokePath :: String -> [Point] -> Picture ()
- fillPath :: FillStyle -> [Point] -> Picture ()
- chop :: Int -> [a] -> [[a]]
- readM :: Read a => String -> Maybe a
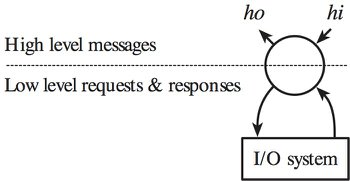
The Fudget type
F hi ho is the type of a fudget that
consumes an high-level input stream of values of type hi and
produces an high-level output stream of values of type ho.
It can also generate a number of user interface elements,
and can read input from and send output to those user interface elements.
Other types
We use the notation a+b for Either a b
Running a fudget
runF is typically used only once in the main function of a program.
It runs the fudget and adds any user interface elements it generates
to the documentBody of the web page.
User interface elements
buttonGroupF :: F hi ho -> F (Click + hi) (Click + ho) #
Creates a button with another fudget inside (which
should be something simple, e.g. an imgF or a stringDisplayF...),
<button>...</button>.
toggleButtonF :: String -> F Bool Bool #
A checkboxF with a label
radioGroupF :: Eq alt => Options alt -> F alt alt #
A group of checkboxes allowing you to select one of several alternatives
radioGroupF' :: Eq alt => Options alt -> F alt alt #
A radioGroupF without the built-in vertical layout
selectF :: Eq alt => Options alt -> F alt alt #
A menu of options, <select><option>...</option>...</select>
dynSelectF :: Eq alt => Options alt -> SelectF alt #
A menu of options that can be modified dynamically
type SelectF alt = F (ListRequest alt) alt #
data ListRequest alt #
sliderF :: Enum a => (a, a) -> F a a #
A slider which lets you choose a value from an enumeration,
<input type="range">
meterF :: (Num i, Ord i, Show i) => (i, i) -> F i o #
A meter for scalar value between given minimum and maximum.
<meter min=... max=...></meter>
stringDisplayF :: F String ho #
An output-only element displaying text, <span>...</span>
htmlDisplayF :: F String ho #
An output-only element displaying HTML content
passwordF :: F String String #
A string input/output field that shows **** instead of the actual
input, <input type="password">
canvasF :: (Int, Int) -> F (Picture ()) (Int, Int) #
Creates a canvas of given width and height. Use the functions
from Graphics.UI.Threepenny.Canvas to draw things. The canvas
produces output on mouseup events
(becase mouseup up seems to work for both the left and
the right mouse button, while click only works for the left mouse
button).
canvasF' :: (Int, Int) -> F (Bool, Picture ()) (Int, Int) #
canvasF with an option to render on top of
or replace the current picture
An image, <img src="url" alt="">
You can change the image dynamically by sending in the URL of another
image.
imgF' :: Attribute -> URL -> F URL o #
An image with extra attributes, <img src="url" ...>.
You can change the image dynamically by sending in the URL of another
image.
Interaction control
focusF :: F hi ho -> F (Bool + hi) (Bool + ho) #
Allows you to observe and control the focus of a fudget. (Focus determines where keyboard input goes.)
eventF :: [Element -> Event b] -> ((Element -> Event b, b) -> ho) -> F hi ho -> F hi ho #
Add event handlers to the elements generated by a fudget. Event types can be imported from Graphics.UI.Threepenny.Events.
Static content
Web page layout
tableF :: Int -> F hi ho -> F hi ho #
A table with n columns. The elements generated by the
argument fudget are placed in separate table cells.
permuteF :: ([Element] -> [Element]) -> F hi ho -> F hi ho #
Rearrange the elements generated by a fudget. Note that Elements
can not be duplicated.
Traditional Fudgets compatibility
shellF :: String -> F hi ho -> F hi ho #
With traditional Fudgets, shellF creates top-level application windows.
With WebFudgets, using shellF is entierly optional. It just puts a
title above another fudget and adds a couple of <div> elements that
can be styled to look like a traditional application window with a
title bar, if you wish.
<div class="shellF"><h4>title</h4><div>...</div></div>
Changing style and other properties
classF :: F hi ho -> String -> F hi ho #
Set the class attribute of the elements generated by a fudget
Fudget plumbing
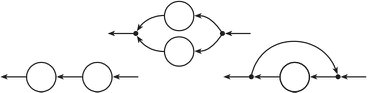
Parallel composition
(>+<) :: F i1 o1 -> F i2 o2 -> F (i1 + i2) (o1 + o2) infixl 5 #
Tagged parallel composition. Messages to/from the left fudget are
tagged Left. Messages to/from the right fudget are tagged Right.
(>+) :: F hi1 ho -> F hi2 p -> F hi1 ho infixl 5 #
Parallel composition where only the left fudget is connected. The right fudget is typically static content.
(+<) :: F hi1 p -> F hi2 ho -> F hi2 ho infixl 5 #
Parallel composition where only the right fudget is connected. The left fudget is typically static content.
listF :: Eq a => [(a, F hi b)] -> F (a, hi) (a, b) #
Tagged parallel composition of a list of fudgets
Serial composition
(=<=) :: F hi1 ho -> F hi2 hi1 -> F hi2 ho infixr 3 #
Right-to-left serial composition. The output stream of the right fudget
is connected to the input stream of the left fudget. This was
originally called >==< in Fudgets.
Loops
loopLeftF :: F (loop + hi) (loop + ho) -> F hi ho #
Creates a feedback loop. loopLeftF fud behaves as follows:
output from fud tagged Left will be sent back to
the input of fud. Output from fud tagged Right will be sent to the
output of loopLeftF fud. Input to loopLeftF fud will be tagged
Right and delivered to fud.
Copy output back to the input. The fudget needs to send on average strictly less than one output message per input message, otherwise it will become busy reacting to its own messages.
loopThroughRightF :: F (Either a hi) (Either b ho) -> F b a -> F hi ho #
loopThroughRightF master slave is similar to loopLeftF master, but
the loop goes through the slave fudget. (A better name might be
encapsulateF since all communication with the slave has to go via
the master, so the slave is encapsulated in this sense.)
loopThroughRightF :: F (ro+hi) (ri+ho) -> F ri ro -> F hi ho
Adding application specific functionality
Stateless
filterF :: (ho -> Bool) -> F ho ho #
Like filter for lists. Propagates values from the input stream to
the output stream if they pass a test.
concatMapF :: (i -> [o]) -> F i o #
Stateful
stateF :: (s -> hi -> (s, [ho])) -> s -> F hi ho #
stateF is used to maintain an internal state.
Given a state transition function f and an initial state s,
stateF f s responds to input by applying f to it to update the
internal state and generate zero or more output messages.
persistentStateF :: (Read s, Show s) => String -> (s -> i -> (s, [o])) -> s -> F i o #
Like stateF, but also uses LocalStorage to retain the state between
activations of the web application. The first argument is a key that should
be unique among all web applications on the same server.
localStorageF :: (Read a, Show a) => String -> a -> F a a #
Outputs one message read from LocalStorage on startup. Writes any input to LocalStorage.
Stream manipulation
After the first Left a and Right b has arrived on the input, gatherF
output pairs (a,b) with the most recent a and b values received.
Timing
Debugging
Internal
These definitions reveals implementation details that might change.
elemDisplayF :: Maybe (UI Element -> UI a) -> F (UI Element -> UI b) o #
Threepenny extras
Attributes
type Attribute = UI Element -> UI Element #
An attribute is a function that modifies a user interface element. See also Graphics.UI.Threepenny.Attributes.
Drawing on a canvas
See also Graphics.UI.Threepenny.Canvas
strokePath :: String -> [Point] -> Picture () #